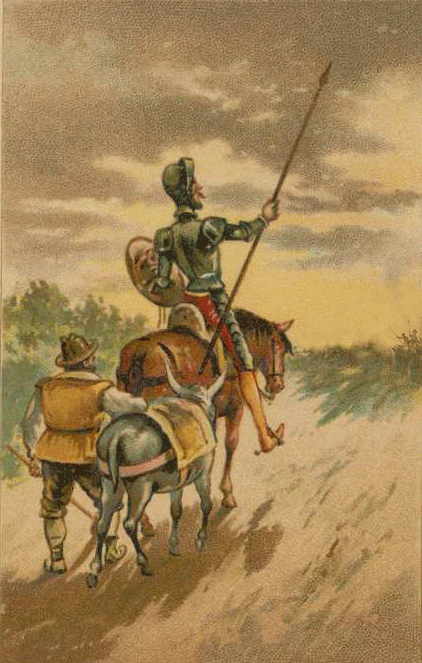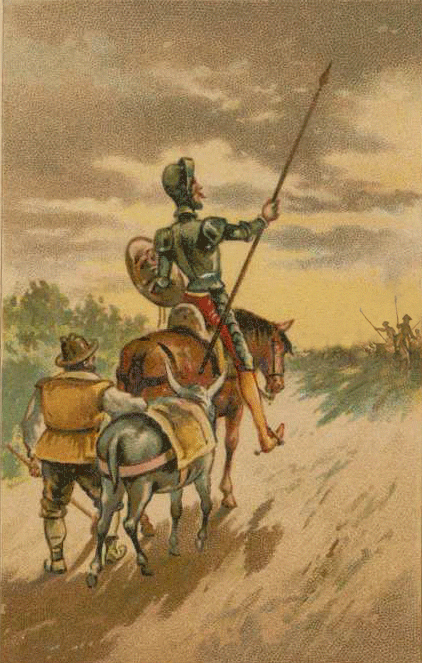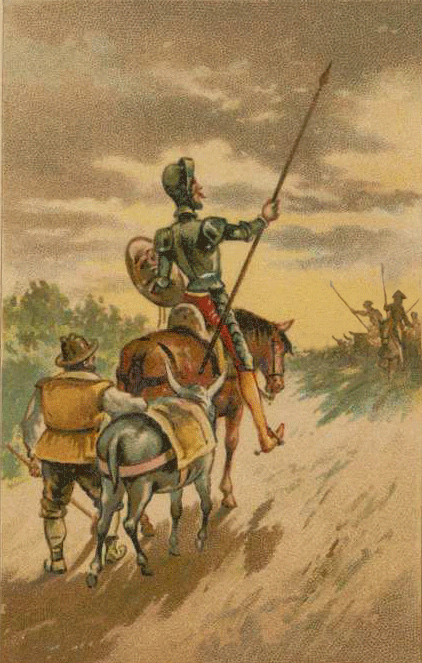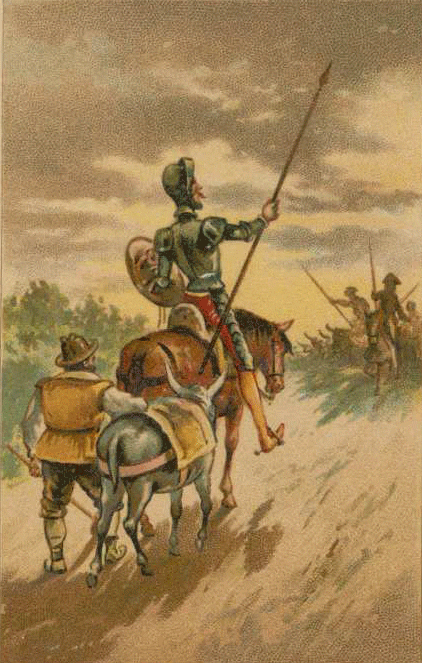
El Quijote, or Don Quixote in English, is a novel by Miguel de Cervantes, published in two parts in 1605 and 1615. It is considered the first modern novel and one of the most influential works of literature in history. The novel tells the story of an aging gentleman who, obsessed with chivalric romances, decides to become a knight-errant and embark on a series of adventures with his faithful squire, Sancho Panza.
The cultural importance of el Quijote lies in its profound impact on the development of the Spanish language, the literary genre of the novel, and the representation of the Spanish identity and values. Some of the aspects that make el Quijote a masterpiece of world literature are:
Its innovative use of the Spanish language, which combines different dialects, registers, and styles, creating a rich and expressive linguistic diversity. Cervantes also coined many new words and phrases that have become part of the common speech, such as quixotic, meaning impractical or idealistic.
Its original structure and narrative technique, which breaks the conventions of the chivalric romance and introduces elements of realism, satire, irony, and metafiction. The novel is composed of various episodes that are interconnected by the characters and themes, but also have their own plot and style. The novel also plays with the notions of authorship, fiction, and truth, as it includes multiple narrators, sources, and perspectives, and challenges the reader’s expectations and assumptions.
Its universal and timeless themes, such as the conflict between reality and imagination, the quest for honor and glory, the value of friendship and loyalty, the critique of social norms and institutions, and the exploration of human nature and psychology. The novel also reflects on the historical and cultural context of Spain in the 17th century, a period of political and religious turmoil, economic decline, and cultural splendor.
Its memorable and complex characters, especially the protagonist, Don Quixote, and his squire, Sancho Panza, who represent the contrast and complementarity between idealism and realism, madness and wisdom, nobility and commonness, fantasy and experience. The novel also features a gallery of secondary characters, such as Dulcinea, the imaginary lady love of Don Quixote, and the innkeeper, the priest, the barber, and the duke and duchess, who interact with the main characters and influence their fate.
Its enduring legacy and influence, which has inspired countless adaptations, interpretations, and homages in various media and languages. The novel has been translated into more than 140 languages and has been the subject of numerous studies and analyses. It has also influenced many writers and artists, such as William Shakespeare, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Gustave Flaubert, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, James Joyce, Jorge Luis Borges, Pablo Picasso, and Salvador Dalí, among others.
In conclusion, el Quijote is a cultural treasure that transcends its time and place, and offers a universal and humanistic vision of life, literature, and art. It is a novel that invites the reader to join the adventure of Don Quixote and Sancho Panza, and to share their dreams, hopes, fears, and joys. It is a novel that celebrates the power of imagination, the beauty of language, and the dignity of the human spirit.
Quiz
Instructions: Answer each question in 2-3 complete sentences.
- What is the significance of Don Quixote in literary history?
- Describe the main character, Don Quixote, and his primary motivation.
- Who is Sancho Panza, and what is his relationship to Don Quixote?
- How does Cervantes utilize language in Don Quixote?
- What are some of the narrative techniques employed in Don Quixote?
- Identify two major themes explored in the novel.
- How does the novel reflect the historical context of 17th-century Spain?
- Briefly describe the characters of Dulcinea, and the innkeeper.
- How has Don Quixote influenced other artists and writers?
- What aspects of the novel make it considered a universal and humanistic work?
Essay Questions
Instructions: Develop a well-organized essay that thoroughly addresses each of the following prompts. Your essay should include a clear thesis statement, supporting evidence from the text, and logical reasoning.
- Discuss the ways in which Cervantes uses the characters of Don Quixote and Sancho Panza to explore the dual nature of human existence.
- Analyze the narrative structure of Don Quixote, focusing on how Cervantes incorporates multiple perspectives and the role of metafiction within the work.
- Examine the cultural and historical significance of Don Quixote, explaining how it reflects the social and political environment of 17th-century Spain.
- Evaluate the impact of Don Quixote on the development of the novel as a literary genre, considering its innovations in style, characterization, and thematic depth.
- Explore the universal and humanistic themes within Don Quixote, and discuss why these continue to resonate with readers centuries after its publication.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Chivalric Romance: A medieval literary genre that typically involves knights, adventures, courtly love, and fantastical elements.
- Knight-Errant: A knight who travels in search of adventure and to demonstrate his chivalry by helping those in need.
- Squire: A young man who acts as an attendant to a knight, learning the arts of knighthood.
- Quixotic: Exceedingly idealistic; unrealistic or impractical, often based on romantic notions.
- Satire: The use of humor, irony, exaggeration, or ridicule to expose and criticize people's stupidity or vices.
- Metafiction: Fiction in which the author self-consciously alludes to the artificiality or literariness of a work by departing from novelistic conventions.
- Irony: The expression of one's meaning by using language that normally signifies the opposite, typically for humorous or emphatic effect.
- Idealism: The practice of forming or pursuing ideals, especially unrealistically.
- Realism: The attitude or practice of accepting a situation as it is and being prepared to deal with it accordingly.
- Humanism: A philosophical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, generally preferring critical thinking and evidence over acceptance of dogma or superstition.

Comments
Post a Comment